 |
      
|
|
Company IMEX in the News Products & Services Client List Analysts Company Links Contact Us Employment Site Map |
|
Overview Expertise Positioning Competitive Profiles Sales Leads |
|
Reports Consulting |
|
Executive Summary | Table of Contents | Order |
|
|
Challenges/CaveatsOne of the major shortcomings of NAS storage architecture is that the network on which NAS runs is also used for data access by clients to retrieve data from the file server or communicate with application servers. The data movement between the disk and tape servers also goes over the same LAN. This creates a major network bottleneck when the number of users increase. Further the overhead of network stack contributes to higher data latency during server or client to storage communications. While NAS works well for documents, file manipulations and transaction based applications, it is not necessarily most advantageous for database applications because it is file-oriented. Also for high bandwidth video applications, NAS slows down since the shared network on NAS gets clogged fast with multiple large files and starts to become a bottleneck. |
SAN - Storage Area Network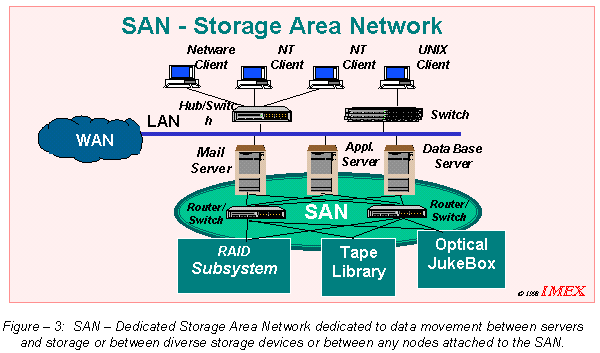
|
|
A SAN (Storage Area Network) is a dedicated high performance network to move data between heterogeneous servers and storage resources. Being a separate dedicated network it avoids any traffic conflict between clients and servers. A fibre channel based SAN combines the high performance of an I/O channel (IOPS and bandwidth) and the connectivity (distance) of a network. PerformanceSAN enables concurrent access of disk or tape arrays by two or more servers at high speeds across fibre channel, providing much enhanced system performance. AvailabilitySAN has disaster tolerance built in since data can be mirrorred using FC SAN up to 10 km away. CostSince SAN is an independent network, initial costs to set up the infrastructure would be higher but the potential exists for rapid cost erosion as SAN installed base increases. ScalabilityScalability is natural to SAN architecture, depending on the SAN network management tools used. InteroperabilityLike a LAN/WAN it can use a variety of technologies such as serial SCSI, ESCON, FICON, SSA, ATM, SONET etc. This allows easy relocation of backup data, restore operations, file migration and data replication between heterogeneous environments. Manageability
Future of SAN
SAN technology, in the future, may also interconnect worldwide with other SAN intranet sites to provide instantaneous replication of corporate data to these remote sites to create a global information system. This would allow local access to fast while being up-to-date. ChallengesAs with all new technologies, SAN developments must rapidly happen in areas of data management, security features, interoperability test suites, availability of VI adapters to improve latency between interconnected servers and the availability of SCSI/Fibre Channel bridges. |
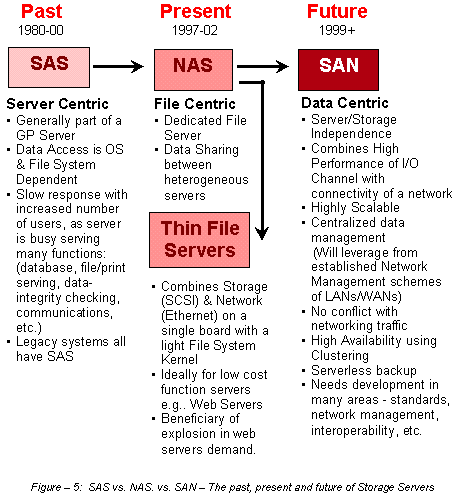
|
|
Additional benefits of NAS for Web Servers accrue when using load balancing and web caching technologies. |
Market Outlook for SAN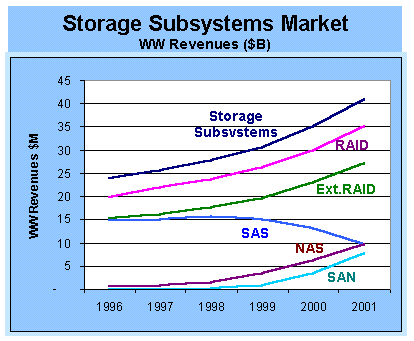
|
|
The market for Storage Subsystems is concentrated in top 10 players. The top 3 players including Compaq (including DEC acquisition), IBM,and EMC alone control 50% of the market. Internal RAID is being led by Compaq, HP and Dell servers. SAN fibre channel products are increasingly being introduced in the market including fibre-channel adapters, hubs, switches and routers, SCSI/FC bridges, disk drives and testers from multiple sources. Eyeing the advantages and popularity of FC/SANs the leading data networking vendors like 3COM have jumped in to embrace the technology. Not far behind would be major players like CISCO, Lucent and Nortel/Bay Networks eyeing the convergence of voice and data networks and associated centralized database servers for interactive voice response and e-commerce applications for the global marketplace. |
All rights reserved © 1997-2011 Reproduction Prohibited. Terms of use.
IMEX Research (408) 268-0800 - Email us
Best Viewed on Internet Explorer 5.0 or Netscape 6 or higher
 SANs create a dedicated network, focused on creating a universal any to any
connectivity between storage and server nodes - a network that combines the
best of mainframe bus and channel's high speed and data integrity benefits with
networks' distance benefits, a network that frees the main LAN network from
backup duties that consume valuable bandwidth, a network that is scalable
allowing increments in capacity without disruptions while leveraging the existing
investments in legacy platforms and existing data, a network that provides
centralized control while providing remote data vaulting for disaster recovery,
a network that offloads storage management tasks from application servers and
speeds up the entire network, thus allowing users the benefit of fast data access.
SANs will eventually be at the core of every enterprise's data center, allowing
companies to design centrally-managed data centers that embrace and interconnect
farflung global SANs and provide service to all of their servers, no matter how
far or no matter what operating systems they are running on.
SANs create a dedicated network, focused on creating a universal any to any
connectivity between storage and server nodes - a network that combines the
best of mainframe bus and channel's high speed and data integrity benefits with
networks' distance benefits, a network that frees the main LAN network from
backup duties that consume valuable bandwidth, a network that is scalable
allowing increments in capacity without disruptions while leveraging the existing
investments in legacy platforms and existing data, a network that provides
centralized control while providing remote data vaulting for disaster recovery,
a network that offloads storage management tasks from application servers and
speeds up the entire network, thus allowing users the benefit of fast data access.
SANs will eventually be at the core of every enterprise's data center, allowing
companies to design centrally-managed data centers that embrace and interconnect
farflung global SANs and provide service to all of their servers, no matter how
far or no matter what operating systems they are running on.
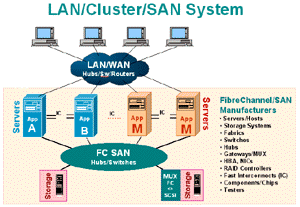 This new focus on data storage, as a key asset to manage, is obvious given the rise
in dollars being spent on storage to the tune of 40-50% of total IT dollars in 1998.
The rise in storage requirements, is being fueled by the birth of incessantly newer
internet, data warehousing and ERP applications and further stoked by the lure of
cheap disk drives at 5 cents per MB at the end-user level today.
This new focus on data storage, as a key asset to manage, is obvious given the rise
in dollars being spent on storage to the tune of 40-50% of total IT dollars in 1998.
The rise in storage requirements, is being fueled by the birth of incessantly newer
internet, data warehousing and ERP applications and further stoked by the lure of
cheap disk drives at 5 cents per MB at the end-user level today.