|
The promise of software-defined data center (SDDC) stipulates on the emergence of an IT infrastructure architecture that leverages a set of new technologies to increase IT agility and speed delivery of new IT services and capacity to application owners while keeping costs down.
Software-defined storage (SDS) is one of the four SDDC components - as are software-defined compute, network, and security. The SDS approach provides benefits across the organization, including: · Autonomy for application owners:
ú Dynamically respond to shifts in demand · Responsiveness for IT teams ú Provision based on priority and service level ú Automate using policy-based security and delegation · Flexibility for purchase decision makers ú Deploy on platform of choice ú Extend capabilities of existing assets
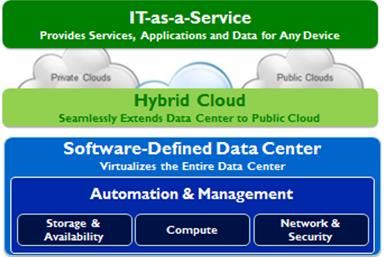
It represents the next logical extension of virtualization and cloud approaches featuring core tenants as: · Resources are defined in software. · Provisioning is based on policy/service levels · Technology runs on a broad range of hardware agnostic platforms · IT-as-a-service provides applications, data for any device and services 24x7
Following stack is a typical representation of IT-as-a-service accessed on-premise or from a hybrid cloud that extends data center to public cloud.
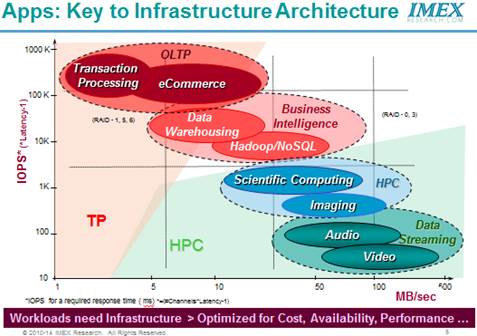
Need: A New Data Center Storage Architecture The nextgen Software Defined Data Center Architecture is based on the principle that by creating an agile, application needs driven infrastructure using industry standard high volume components, CIOs can dramatically reduce costs while increasing productivity and efficiency and addressing business critical mission priorities. It provides a system-level framework that addresses data center demands for consolidation and business continuance in the short term while targeting Infrastructure Services and Application Services implementation to enable emerging Service-Oriented Architectures (SOAs) and On-demand, Software as a Service (SaaS) Cloud Computing technologies. Virtualization is a major disruptive technology of great transformational potential in delivering compelling benefits of significantly improving TCO and ROI in IT organizations since. Hypervisor in Virtualized Data Center Environments Has: - An Inherent knowledge of Application’s Requirements - A Global View of Infrastructure - Is Hardware Agnostic
Storage Underperforms in VM Environments • Very Random, Write intensive I/Os from some VMs get blended with Sequential, Read Heavy I/Os from other VMs resulting in:
- Legacy Soln: Larger, more expensive storage configs created to meet needed IOPs - Storage Capacity wastage • Other Negative Effects - Poor Thin Provisioning & Snapshots/Cloning - Inefficient VM Management Solution - A Storage Hypervisor Create a storage abstraction layer - Do for Storage like Hypervisor for Compute Virtualizes Storage for Optimum Mgmt. - Unlock the Performance & Wasted Capacity of Existing Storage by provisioning Storage as fast as VMS can be created - Improves storage performance by 10x - Improves Thin Provisioning & Snapshots - Reduces capacity consumption up to 90% Provide a VM-Centric Management paradigm - VM-Centric Management - Integrate Seamlessly into existing Hypervisor
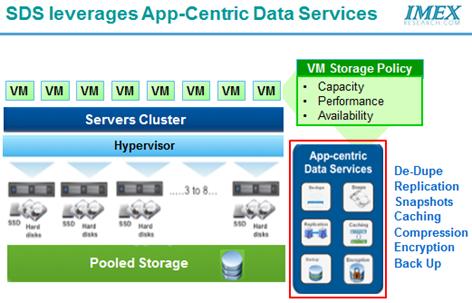
Benefits of deploying Software Defined Storage in SDDC Some of the major benefits inherent in deploying SDS architecture include: · Cost Efficient - Commoditized persistent data storage · Service based architecture · Open standards and interfaces based platform · Focus on IT solution rather than on technical platform · Highly Resilient and Self-Healing · Hypervisor driven Awareness between Application SLA requirements and Resources availability · Highly scalable (capacity, throughput, performance) · Ability to cover multi-storage media formats (blocks, file and object storage) · Highly Automated – Lights Out Storage Operations Capability without Manual Intervention · Removes random write I/Os to mitigate storage I/O inefficiencies from the standard hypervisor · Thin provisions Virtual Disks to outperform VMDKs to cut storage costs in half while providing transparent VMDK level management · Lowers VDI costs by up to 50% · Enables continuous data protection through scalable highly performing snapshots/cloning · Provides instant provisioning of high performance storage for I/O intensive workloads SDS’s
fit in the Enterprise
-On-Premise to Public Cloud Centers
New Goals for the Mobile Cloud Era In the Mobile-Cloud Era, the new goals of On-Premise Infrastructure include: Cost Effectiveness - Public Cloud Storage Cost and scale economics to be available in On-Premise/Private Cloud - Adoption of Public cloud design points right-sized in Private cloud solutions Driving Down Operational and Management Costs - Automation and Self-Service capabilities to reduce scale-out and management complexities arising from manually driven operations - Auto recovery, self-healing architecture for 24x7 uptime operations Adoption of Industry Standards based Infrastructure - Unification of Servers and Storage Management using single pane of dashboard - Reduction of costs using Open Compute Initiatives Roadmap for Migration from Legacy to Modern SDS Infrastructure - Capabilities and Tools for migration from Legacy to Software Defined Storage encompassing - Traditional Architecture: FC/iSCSI SAN Storage (Block Based) - Modern Architecture: SDS in Cluster File Servers (File Based) - Next Gen Architecture: SDS in Cluster File Servers (Object Based) - Future Proofing to include future generations of Flash (3D NAND and NVMe) and High Speed Ethernet (10/40/100 Gbps) and Infiniband and low latency RDMA technologies.
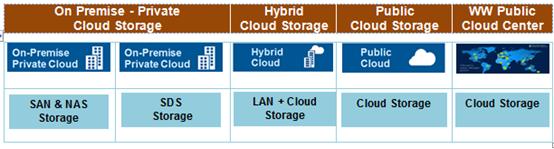
Despite the inherent and obvious advantages of SDS architecture in significantly improving both CapEx through ability use industry standard high volume components to lower costs and OpEx through automation to deploy storage efficient technologies, one of the key challenges for SDS lies in as to how to create a smooth transition from deeply rooted legacy SAN storage architectures into the modern SDS based storage infrastructure. Industry will follow a cascaded transition in stages over time from On Premises Storage to Public Cloud Storage to Public Cloud Centers hosted by Service Providers as depicted in the following diagram.
. IMEX Industry Report – SDS 2014 IMEX Research‘s Industry Report on Software Defined Storage 2014 addresses the need to fully understand the directions IT industry vendors will take in formulating products to meet the need of the demands of CIOs and Datacenter operations.It enumerates a number of metrics for data center to achieve and provides detailed guidance for IT infrastructure vendors and IT decision makers (CIOs and operations managers) on how to optimally deploy compute, storage, intelligent information networks and software technologies that best support their mission needs through optimizing IT resources and business processes. Subjects analyzed · Strategic vision: what issues, opportunities, and threats do new SDDCs force as they evolve over next 5-10 years? · SW Defined DC/SDS Storage Technology trends: what are the technologies for the next-generation datacenter? · Enterprise architecture: What are the datacenter infrastructure requirements? Prescriptive guidance based on experiences of early adopters in implementing managing SDDC · Case Studies: Experiences of early adopters of implementing and managing data center using profiles of some leading US data centers · Best Practices Implementing and Managing SDS - best practices for configuring and managing in test, development and production · SDS Vendors: Products, profiles and strategies.
Major chapter include: 1. Executive Summary
|
||||||||
|
|