The Rise of Blade Computing
Part 1 of 3. Part 2 (Blade Server Technologies) and Part 3 (Future of Data Center) to follow.
Click on Executive Summary, TOC, References, and keynote presentation for additional information.
Doing
More with Less
Until recently,
most data center computing has been performed by expensive, monolithic
mainframe or UNIX SMP servers, fine tuned to run few specific workloads
efficiently.
Pressured by CEOs to “do more with less” in this challenging economic environment improving the productivity of IT assets has become a top priority for CIOs, given the average CPU running around 25% capacity while stranded direct-attached storage being utilized below 50% in many large companies.
Deploying a multitude
of rack-mount xU-servers, each running their own OS on their own individual
hardware, has been
no solution either, since they could not scale due to lack of a shared
fabric backplane.
The real cost reduction opportunity in computing lies in eliminating monolithic, proprietary servers altogether. Replacing them with standard high volume, low-cost, modular servers running industry-standard Windows/Linux OS and augmenting them with advanced access, availability, and administration functions, emulated from expensive mainframe or UNIX environments, will bring about the best of all worlds.
One of the key contributions offered by the new generation of blade servers lies in their ability for hardware provisioning through segmenting server resources at the blade board level. Each of these blade resources may be allocated to one of the operating system instances while achieving scalability through simple plug-ins of additional blades. This form of provisioning provides a high degree of fault tolerance, simplifies the hardware upgrade process, and allows hardware to be logically partitioned to run different applications at different performance levels.
Thus, a diversity of shifting peak loads can simply be handled flexibly through software provisioning of these blade resources. This puts the blade servers at a distinct advantage for adoption in a variety of environments from small
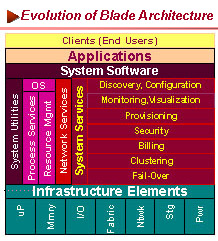
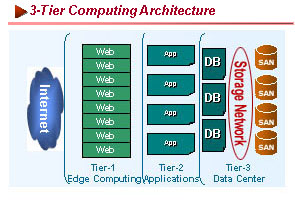
Because of their flexibility to take on software provisioning, blade servers can easily address various specialized requirements of Tier 1, 2 and 3 applications, on the Web or in the Data Center.
Industry standard blades actually facilitate convergence of computing (channels) and Networks (nodal interconnectivity) to achieve true distributed computing as epitomized ultimately in grid computing of the future.
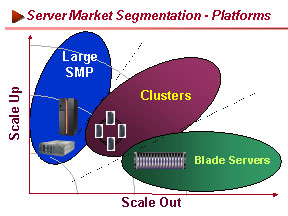
Market
Segmentation by Platform
The emergence of low-cost
Linux/Windows-based volume servers and clustering/interconnect fabric
technologies, together with virtualization and software provisioning,
is allowing blade servers to be adapted in various applications addressing
different vertical markets. These applications include OLTP, decision
support, numeric intensive computing, and streaming content.
Growth
Drivers for Blade Servers
The integrated modular
architecture of blade systems providing Virtualization, Provisioning and
Self-Driven Automation capabilities already are starting to strike a pleasant
chord with CIOs.
Some of the major growth
drivers accelerating the adoption of blade servers include:
For additional information, click on IMEXResearch.com or email us. Tel: (408) 268-0800
Click on the following for additional information or go to http://www.imexresearch.com.
